Some brands of Chinese consumers are looking for growth abroad, in markets such as the US and Southeast Asia.
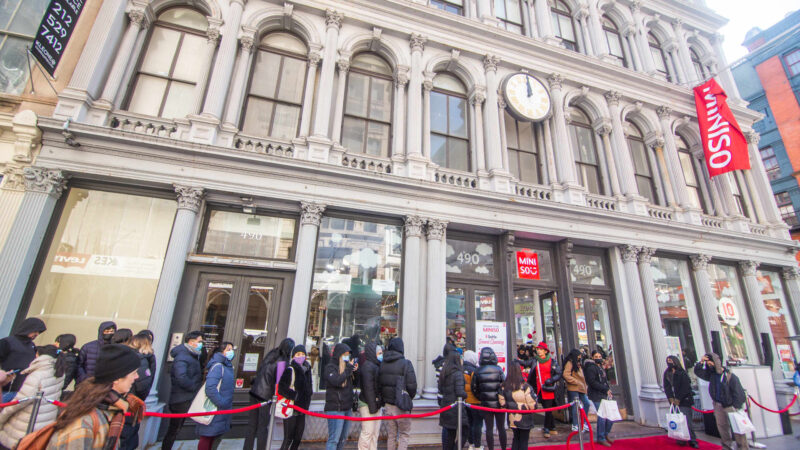
Take Miniso, a toy seller and household product based in Guangdong. Sometimes -sometimes called Muji China, Miniso opened the main shop in Soho New York City in February.
Value of Shop Dirty merchandise – Sales measures from time to time – record around $ 500,000 a month, with $ 1 million a month possibly in December, founder and CEO Jack Ye told CNBC at the end of June.
More importantly, he said that for shops that are operated directly in the United States, Miniso’s gross profit margin is far above 50%.
If we can get a strong footing here and create a good business, we will not have problems in the US as a whole,” said Ye in Mandarin, according to the CNBC translation. The goal is to be the first retailer “$ 10 and under” worldwide.
Miniso shop began to appear in mainland China almost 10 years ago, with foreign expansion starting in 2015 in Singapore. In March, the company said 37% of 5,113 shops abroad.
Like many businesses, Miniso saw sales down during Pandemi. More than two thirds of his income still originated from China. But in recent months, data shows a relatively fast pickup internationally versus domestically, the results of various pandemic effects.
In the nine months ended March 31, the company said, China’s revenue grew by 11% from year to year to 5.91 billion yuan, compared to 48% growth abroad to 1.86 billion yuan.
Chinese retail sales have been lagging behind Pandemi starting in 2020. The decline in the housing market does not help. The tendency of local residents to save, instead of spending or investing, has risen to the highest in 20 years”Chinese companies that develop into foreign markets will be the main trend going forward,” said Charlie Chen, head of consumer research in China Renaissance. “China has actually entered a relatively rich stage with a relatively high GDP per capita.”
He showed that for products such as AC, penetration between rural households was 73.8% in 2020 – and even higher in 149.6% in urban areas. China Renaissance hopes that the level of penetration will increase steadily in the next few years.
There is a little additional volume or additional request that can be made in China in a short time,” Chen said. “For AC, this home equipment company, where they can get more income, abroad.”
In Southeast Asia, AC has a household penetration rate of 15%, according to the International Energy Agency.
Midea, Hisense and Haier Smart Home household appliances companies have entered markets outside China over the past few years. Haier even acquired the General Electric tool unit for $ 5.4 billion in 2016. The purpose of Hisense was that in 2025, foreign markets would generate half of his total income.
Obviously if [Chinese companies] want to enter the foreign market, [they] need to build their brand, need to fight with existing competitors,” Chen said. “Costs will not be low. Initially they would not be profitable. But they invest. “
If the Chinese business can build their brand abroad, they can compete with a lower selling price because they have or work directly with factories in China. It has helped companies like Shein become an international e-commerce giant.
Likewise, Miniso Ye said his strategy in the US combined the company’s supply chain network in China with the work of New York designers – so that the product could switch from design to the shelf to store in about three months.
The process can take six months or even one year if the design company needs to find its own factory, you claim.